Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (32): 5237-5243.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.32.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Parental peripheral blood haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in treatment of children with relapsed and refractory acute leukemia
Wan Ding-ming, He Hai-yan, Bian Zhi-lei, Xie Xin-sheng, Sun Ling, Sun Hui, Cao Wei-jie,Xuan Zhong-qian, Liu Fei
- Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2014-07-08Online:2014-08-06Published:2014-09-18 -
Contact:He Hai-yan, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China Wan Ding-ming and He Hai-yan contributed equally to this work. -
About author:Wan Ding-ming, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hematology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wan Ding-ming, He Hai-yan, Bian Zhi-lei, Xie Xin-sheng, Sun Ling, Sun Hui, Cao Wei-jie,Xuan Zhong-qian, Liu Fei. Parental peripheral blood haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in treatment of children with relapsed and refractory acute leukemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(32): 5237-5243.
share this article
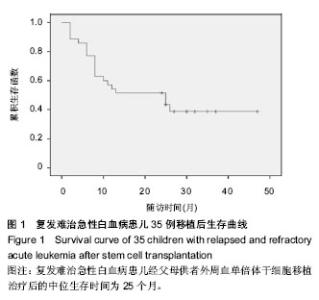
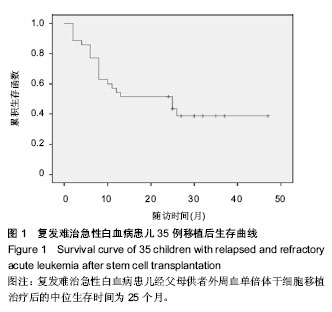
2.1 患者数量分析及患者临床信息 共纳入35例儿童复发难治急性白血病行父母供者外周血单倍体造血干细胞移植,均进入结果分析,无数据脱落。患儿基本信息见表1。 2.2 儿童复发难治急性白血病患者的回输细胞数量 回输单个核细胞中位数为5.82(3.23-8.45)×108/kg,CD34+细胞中位数4.52(2.37-11.51)×106/kg;其中3例患者回输外周血干细胞小于4×108/kg,10例患者CD34+细胞小于4×106/kg,患者造血干细胞仍植入成功。 2.3 儿童复发难治急性白血病患者的植入情况 以持续 3 d中性粒细胞≥0.5×109 L-1,连续3 d不输注血小板,血小板≥20×109 L-1,作为造血功能重建的指标[18]。中性粒细胞中位植入时间为13(9-20) d,血小板中位植入时间14(10-58) d。所有患者经微卫星标记、性染色体及血型检测为完全供者嵌合体[35-36],证明造血重建成功。 2.4 儿童复发难治急性白血病患者的移植物抗宿主病发生情况 干细胞回输后前100 d内35例患儿中23例出现急性移植物抗宿主病,发生中位时间为48.5(27-85) d,其中Ⅰ-Ⅱ度12例,8例以皮肤为主,4例以肠道为主,发生率为34.3%;Ⅲ-Ⅳ度13例,3例以皮肤为主,9例以肠道为主,1例以肝脏为主,发生率为37.1%;急性移植物抗宿主病累积发生率为65.7%;干细胞回输后随访2-47个月,15例出现不同脏器不同程度慢性移植物抗宿主病,发生时间中位数为121(98-360) d,其中4例广泛型皮肤慢性移植物抗宿主病,11例为局限型慢性移植物抗宿主病,多见于口、眼、皮肤,总发生率42.9%。发生移植物抗宿主病的患儿中2例死于腹泻,均为急性肠道排斥反应。 2.5 儿童复发难治急性白血病患者的原发病复发情况 随访至2014年1月,移植后半年内共有6例复发,均为骨髓象复发,3例为急性B淋巴细胞白血病(BCR/ABL阳性),2例为复发B急淋,1例为慢粒急淋变;移植半年后6例复发,其中2例为复发急性B淋巴细胞白血病中枢神经系统侵犯,接受放疗,2例M5为粒细胞肉瘤,给予化疗+放疗;2例骨髓象复发,1例为M2合并BCR/ABL阳性,1例为复发B急淋。总复发率达34.3%。 2.6 儿童复发难治急性白血病患者的不良反应 儿童复发难治急性白血病行父母供者外周血单倍体造血干细胞移植35例,6例死于重度感染(其中肺部感染3例,肠道感染1例,中枢神经系统感染2例);2例死于超急性移植物抗宿主病肠道反应;1例死于移植后淋巴细胞增殖性疾病;1例因应用蒽环类药物导致心肌损伤,进而心脏骤停;2例患儿出现癫痫样抽搐;2例发生皮肤黑曲霉菌感染,其中1例死于多脏器功能衰竭;2例发生纯红再障,分别在干细胞移植后7个月,11个月后血红蛋白恢复至正常范围。 2.7 儿童复发难治急性白血病患者的临床疗效 35例患者随访2-47个月,移植相关死亡率14.3%,2年无白血病生存率为42.9%,2年总体生存率为51.4%,中位生存时间为25个月;生存曲线见图1。"
| [1] 顾龙君.儿童急性淋巴白血病诊疗建议[J].中华儿科杂志,2006, 44(5): 392-396. [2] 卢新天.儿童高危急性淋巴细胞白血病治疗策略[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2013,45(2):327-332. [3] 汤静燕,薛惠良,陈静,等.儿童B系急性淋巴细胞性白血病SCMC-ALL-2005方案评估[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(8): 546-550. [4] Gorman MF, Ji L, Ko RH, et al. Outcome for children treated for relapsed or refractory acute myelogenous leukemia (rAML): a Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia (TACL) Consortium study. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010;55(3): 421-429. [5] 王昱,刘开彦,许兰平,等.异基因造血干细胞移植治疗高危恶性血液病[J].中华内科杂志,2007,46(11):903-906. [6] 黄晓军,刘代红.人类白细胞抗原不合或单倍体亲属供者造血干细胞移植[J].临床内科杂志,2006,23(9):581-583. [7] 陈惠仁.单倍型造血干细胞移植的新进展及其临床研究结果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(34):6735-6738. [8] 李慧文.遴选和回访对提高造血干细胞捐献者资料库有效率的探讨[J].中国输血杂志,2009,22(11):937-938. [9] Laughlin MJ, Barker J, Bambach B, et al. Hematopoietic engraftment and survival in adult recipients of umbilical-cord blood from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344(24): 1815-1822. [10] Lu DP. Blood and marrow transplantation in mainland China. Hong Kong Med J. 2009;15(3 Suppl 3):9-12. [11] Rubinstein P, Carrier C, Scaradavou A, et al. Outcomes among 562 recipients of placental-blood transplants from unrelated donors. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(22):1565-1577. [12] 孙巍,王晓华.父供子单倍体异基因造血干细胞移植治疗高危白血病2例临床分析[J].中国小儿血液与肿瘤杂志,2013,18(3): 135-138. [13] 刘代红,黄晓军.亲属HLA单倍体相合/部分相合造血干细胞移植进展[J].中华器官移植杂志,2010,31(2):125-127. [14] 黄晓军.造血干细胞移植的挑战及对策[J].中华血液学杂志,2013, 34(2):89-92. [15] Huang XJ. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in China: current status and prospects. Am J Blood Res. 2011;1(1):90-97. [16] Lu DP, Dong L, Wu T, et al. Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood. 2006;107(8): 3065-3073. [17] 王昱,刘代红,刘开彦,等.单倍型异基因造血干细胞移植治疗难 治/复发急性白血病患者的疗效观察[J].中华血液学杂志,2012, 11(33):917-921. [18] Liu DH, Xu LP, Liu KY, et al. Long-term outcomes of unmanipulated haploidentical HSCT for paediatric patients with acute leukaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(12): 1519-1524. [19] van Walraven SM, Ball LM, Koopman HM, et al. Managing a dual role--experiences and coping strategies of parents donating haploidentical G-CSF mobilized peripheral blood stem cells to their children. Psychooncology. 2012;21(2): 168-175. [20] Cavazzana-Calvo M, André-Schmutz I, Fischer A. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for SCID patients: where do we stand? Br J Haematol. 2013;160(2):146-152. [21] 张之南,沈悌.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M].3版.北京:科学出版社, 2008. [22] 吕善根.儿童难治性急性白血病的诊断和治疗[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2002,17(6):325-326. [23] Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, Burchielli E, et al. NK cell alloreactivity and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40(1):84-90. [24] Chang YJ, Huang XJ. Use of G-CSF-stimulated marrow in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation settings: a comprehensive review. Clin Transplant. 2011;25(1):13-23. [25] 王智明,王琳,徐丹丹,等.改良预处理方案在单倍体移植治疗恶性血液病中的应用[J].中国医药,2010,65(6):527-529. [26] 万鼎铭,石聪聪,谢新生,等.父母供子女单倍型造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10):1753-1760. [27] 万鼎铭,索金燕,孙慧,等.同胞相合移植单个核细胞和CD34+细胞输入数量与造血重建的关系[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2010, 15(4):654-655. [28] Thomas E, Storb R, Clift RA, Fefer A, et al. Bone-marrow transplantation (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975; 292 (16):832-843. [29] 黄晓军,陈育红,韩伟,等.人类白细胞抗原不相合造血干细胞移植治疗白血病的临床研究[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2003,35(2): 115-118. [30] Ji SQ, Chen HR, Wang HX, et al. G-CSF-primed haploidentical marrow transplantation without ex vivo T cell depletion: an excellent alternative for high-risk leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30(12):861-866. [31] 万鼎铭,张诚,谢新生,等.单倍体相合造血干细胞移植治疗高危白血病[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2011,15(19):3485-3488. [32] 施继敏,景晶,罗依,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后并发出血性膀胱炎的高危因素和防治措施[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(3): 148-151. [33] 万鼎铭,周雪芳,谢新生,等.异基因造血干细胞移植后肠球菌相关性腹泻的临床分析[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2014(2):284-287. [34] Wang Y, Liu DH, Xu LP, et al. Superior graft-versus-leukemia effect associated with transplantation of haploidentical compared with HLA-identical sibling donor grafts for high-risk acute leukemia: an historic comparison. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17(6):821-830. [35] 许兰平,黄晓军.干细胞移植的HLA配型和植入证据检测[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2005,20(11):649-651. [36] 汪定春,刘霆.造血干细胞移植后植入证据检测方法的研究现状[J].中国输血杂志,2003,16(1):54-57. [37] 陈惠仁,何学鹏,司英健,等.单体型造血干细胞移植治疗儿童白血病研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2008,35(3):293-294. [38] 刘代红,刘开颜,许兰平,等.亲属单倍体非体外去T细胞造血干细胞移植治疗儿童恶性血液病[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2009, 41(3):291-296. [39] Stern M, Ruggeri L, Mancusi A, et al. Survival after T cell-depleted haploidentical stem cell transplantation is improved using the mother as donor. Blood. 2008;112(7): 2990-2995. [40] Wang Y, Liu DH, Xu LP, et al. Haploidentical/mismatched hematopoietic stem cell transplantation without in vitro T cell depletion for T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18(5):716-721. [41] Zhang C, Zhang X, Chen XH. Cellular mechanism for granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in the prevention of graft-versus-host disease in combined bone marrow and peripheral blood transplantation for hematological malignancies: the composition in collection. Transfus Apher Sci. 2013;48(1):3-9. [42] Di Bartolomeo P, Santarone S, De Angelis G, et al. Haploidentical, unmanipulated, G-CSF-primed bone marrow transplantation for patients with high-risk hematologic malignancies. Blood. 2013;121(5):849-857. [43] Zhang C, Zhang X, Chen XH, et al. Factors influencing engraftment in HLA-haploidentical/mismatch related transplantation with combined granulocyte-colony stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood and bone marrow for patients with leukemia. Transfus Apher Sci. 2011;44(3):249- 255. [44] 孙于谦,刘代红,许兰平,等.重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子动员的供者外周血采集物治疗异基因造血干细胞移植后植入功能不良的疗效和安全性[J].中华内科杂志,2013,52(9):730-733. [45] Aversa F, Terenzi A, Tabilio A, et al. Full haplotype- mismatched hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: a phase II study in patients with acute leukemia at high risk of relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(15):3447-3454. [46] Kanda Y, Chiba S, Hirai H, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from family members other than HLA-identical siblings over the last decade (1991-2000). Blood. 2003;102(4):1541-1547. [47] Huang XJ. Current status of haploidentical stem cell transplantation for leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2008;1:27. [48] 徐应永,陈静,薛惠良,等.FLAG方案治疗小儿复发难治性急性白血病临床研究[J].癌症进展,2010,8(3):279-284. |
| [1] | Tian Qinyu, Tian Xinggui, Tian Zhuang, Sui Xiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Xiaobo, Guo Quanyi. Protection of manganese oxide nanoparticles for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell spreading against oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 821-826. |
| [2] | Fu Chunmei, Zhang Pu, Wang Yang, Li Xiaolin, Xue Yan, Fu Jie, Zhang Cixian, Yang Yujuan, Duan Yaya, Feng Kai. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of 24 patients with severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 15-20. |
| [3] | Huang Chuwen, Jiang Hua, Li Minqing. Complications and death causes of peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of thalassemia major [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 42-48. |
| [4] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [5] | Wen Jianyun, Miao Lili, Guan Di, Liu Xuan, Chen Libai, Feng Xiaoqin, Xu Xiaoxiao, Liu Qiujun, Wu Xuedong, He Yuelin. Correlation of the level of plasma biomarkers with acute graft-versus-host disease in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5032-5039. |
| [6] | Wu Huiting, Zhu Dacheng, Xu Xiaoming, Chang Na. Ethanol extract of toosendan induces apoptosis of leukemia CEM cells through mitochondrial pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4873-4878. |
| [7] | Chen Dabing, Yang Ting. Immune reconstruction and anti-cytomegalovirus immunity of mesenchymal stem cells after transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4052-4057. |
| [8] | Xu Anhui, Lin Xiuxiu, Zhang Xuhan, Song Kaidi, Sun Guangyu, Tang Baolin, Sun Zimin, Zheng Changcheng. Mechanism of separation of graft-versus-host disease and graft versus leukemia in unrelated cord blood transplantation for hematological malignancies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 1993-1999. |
| [9] | Xu Huimin, Zhang Suping, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Zhang Ran, Wang Yiran, Wan Dingming. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a single-arm clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4921-4927. |
| [10] | Li Ye, Yang Yukun, Zhu Xiangqing, He Jie, Wang Jinxiang, Wang Yanying, Tian Chuan, Pang Rongqing, Pan Xinghua. In vivo track technique for mesenchymal stem cells: how to realize simultaneous tracing of distribution and survival [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5025-5033. |
| [11] | Chen Xiao, Guo Zhi, Chen Lina, Liu Xuanyong, Zhang Yihuizhi, Li Xumian, Wang Yueqiao, Wei Liya, Xie Jing, Lin Li. Factors affecting the mobilization and collection of autologous peripheral blood hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2958-2962. |
| [12] | Sun Weixing, Zhao Yongchao, Zhao Ranzun. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of myocardial infarction: problems, crux and new breakthrough [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3103-3109. |
| [13] | Cao Linlin, Ding Kaiyang, Song Hao, Wu Guolin, Hu Maogui, Fan Dandan, Zhou Chenyang, Wang Cuicui, Feng Yuanyuan. Efficacy and influencing factors of autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of malignant lymphoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1993-1998. |
| [14] | Zhang Wenjian, Ma Lingfu, Wang Zhimin, Mo Wenjian, Zhou Ruiqing. Muscle mass evaluation and influencing factors of sarcopenia in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1999-2004. |
| [15] | Zhang Xuhan, Wang Li, Tang Baolin, Wan Xiang, Yao Wen, Song Kaidi, Sun Zimin. Pretreatment of unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation without antithymocyte globulin for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: follow-up evaluation of 306 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4986-4993. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||